Quickstart step 2 : Android minimum code
Here are the steps required for a minimum integration of the Veery Geo-predictive SDK inside your Android application.
Prerequisites
You should have requested your Developer API Key and received it in the following format:
| YOURCOMPANY ACCESS KEY | Where to use in Android Studio | Value (example) |
|---|---|---|
| CLIENT_ID | AndroidManifest.xml | 00000000-1234-abcd-efbh-1234567890ab |
| API_KEY | AndroidManifest.xml | abcdef12-0123-4567-890a-bcdef1234567 |
| API_SECRET | MainActivity.java -> veery.setApiKeySecret(...) | SuPeRScrET12345789GhJ |
These will be used in the next steps of the Veery integration.
build.gradle
In your Android studio project, you should
- Declare the Roofstreet bintray repo as a maven source
- include Veery library (veery:X.Y.Z@aar)
- include google play service (play-services:11.4.2)
- include google maps utils : (android-maps-utils:0.4+)
in your build.graddle (Module:app) you should add the following lines inside the Android section:
android { repositories { maven { url 'https://dl.bintray.com/roofstreet/maven/' } } dependencies { compile 'com.google.maps.android:android-maps-utils:0.4+' compile 'com.google.android.gms:play-services:11.4.2' // X.Y.Z should be the last android release compile 'com.roofstreet.android:veery:X.Y.Z@aar' } }
Note : "X.Y.Z" should be replaced by the latest android release.
AndroidManifest.xml
In your AndroidManifest.xml file you shoud add the following (using the credentials received from your API KEY registration):
<application ... ... <meta-data android:name="com.roofstreet.veery.API_KEY" android:value="abcdef12-0123-4567-890a-bcdef1234567" /> <meta-data android:name="com.roofstreet.veery.CLIENT_ID" android:value="00000000-1234-abcd-efbh-1234567890ab "/> <meta-data android:name="com.roofstreet.veery.ENVIR" android:value="sandbox"/>
The environment should be "sandbox" unless you have received the agreement from Roofstreet to use a production platform.
Enable Firebase Cloud Messaging
If you did not included firebase notifications in your application yet, you should do the following:
In Android Studio, Use the menu item Tools > Firebase > Cloud Messaging > Set up Firebase Cloud Messaging (require Android studio 2.3.3 minimum)
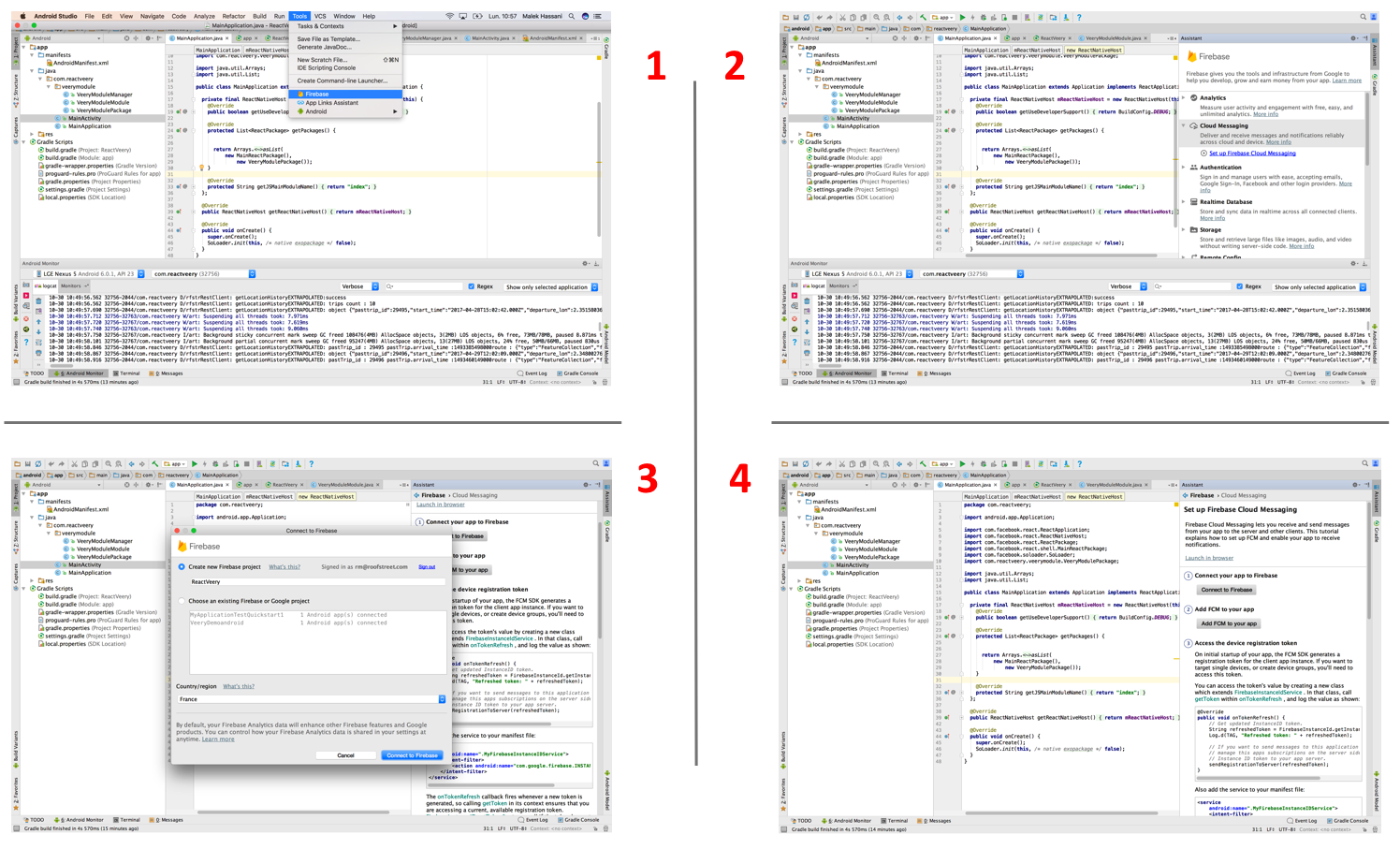 .
.
This procedure will create the two classes MyFirebaseInstanceIDService and MyFirebaseMessagingService required in the next steps.
MyFirebaseInstanceIDService.java
The FirebaseInstanceIdService class is used to receive the FCM device token that Veery requires to
- Silently communicate with the Veery Backend (receive internal events)
- Send Push Notifications to your users if you decided to use Veery for the Notifications
So the following step is mandatory or Veery will not properly work within your application.
// TODO : Import the Veery Library import com.roofstreet.android.veery.Veery; public class MyFirebaseInstanceIDService extends FirebaseInstanceIdService { // TODO : Declare a persistant Veery Object Veery veery = new Veery(this); @Override public void onTokenRefresh() { // TODO : Let Veery know the Device Token veery.setFirebaseToken(FirebaseInstanceId.getInstance().getToken()); } }
MyFirebaseMessagingService.java
The FirebaseMessagingService class is used when receiving a Push notification.
Veery Uses Silent notifications to save battery and geolocalize or comunicate only when the predictive backend requires it.
So the following code redirect the notifications to the Veery Agent. If the agent note that the notification, it returns true so you know this message does not concerns another framework or your own code.
// TODO : Import the Veery Library import com.roofstreet.android.veery.Veery; public class MyFirebaseMessagingService extends FirebaseMessagingService { String TAG = "MyFirebaseMessagingService"; // TODO : Declare a persistant Veery Object Veery veery = new Veery(this); @Override public void onMessageReceived(RemoteMessage remoteMessage) { // TODO : if veery can handle the notification, just return if (veery.firebaseMessageHandler(remoteMessage)) return; // Veery did not recognize the notification so it comes from another framework // Your own Handle code here } // There is more code generated by android studio here (no change) }
MainActivity.java
The Following code is required in the Main activity of your application (Could be a MapsActivity for Google maps apps):
- Connect and disconnect the Veery agent service when the app is starting or stopping
- Set the API Key Secret
- Activate the required functionalities (see ) (foreground geolocation, background geolocation, geoprofiling, predictive geolocation)
Include the library and create the veery object
In your MainActivity.java, add the following
// TODO : Import android.location and veery library import android.location.Location; import com.roofstreet.android.veery.*; public class MapsActivity extends AppCompatActivity { // ... // TODO : Inside the Activity Class (as a class member variable !!not inside a function!!) private final Veery veery = new Veery(this); // ... }
onCreate : Connect the service, declare the API Secret and start firebase
In your MainActivity.java, add the following
public class MapsActivity extends AppCompatActivity { private final Veery veery = new Veery(this); protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); // ...Some initialization here... // TODO : Connect to the service and start it if it was off veery.serviceConnect(); // TODO : declare your API KEY Secret veery.setApiKeySecret("SuPeRScrET12345789GhJ"); // TODO : initialize firebase FirebaseApp.initializeApp(this); // TODO Let veery know the Firebase token veery.setFirebaseToken(FirebaseInstanceId.getInstance().getToken()); // ...Some initialization here... } // ... }
Activate the required functionality level
Requires Android Veery 1.3.2
1 - Check your Geolocation mode
- FOREGROUND_GEOLOC : geolocalize the user only when the application is in foreground.
- BACKGROUND_GEOLOC : geolocalize the user also when the application is in background.
2 - check veery backend services needed to your App
- COLLECT : Veery will be connected to the backend for historization.
- ROUTE_MATCH : Veery will receive trips computations.
- POINT_OF_INTEREST : Veery will receive Points of interests.
- PREDICTION : Veery will receive Predictions.
Backward compatibility (older than Android Veery 1.3.2)
- FOREGROUND : This is equivalent to Veery.FOREGROUND_GEOLOC.
- BACKGROUND : This is equivalent to Veery.BACKGROUND_GEOLOC.
- BACKEND : This is equivalent to BACKGROUND + Veery.COLLECT + Veery.ROUTE_MATCH.
- GEOPROFILE : This is equivalent to BACKEND + Veery.POINT_OF_INTEREST + Veery.PREDICTION.
You can do that operation whenever you want to activate the user but you should notice that android will request for required the user rights when called.
public class MapsActivity extends AppCompatActivity { private final Veery veery = new Veery(this); protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); veery.serviceConnect(); veery.setApiKeySecret("SuPeRScrET12345789GhJ"); FirebaseApp.initializeApp(this); veery.setFirebaseToken(FirebaseInstanceId.getInstance().getToken()); // TODO : Activate the required function levels (user will be requested to accept geolocation) // veery.activate(Veery.GEOPROFILE); // Requires Android Veery 1.3.2 //veery.activate(Veery.BACKGROUND_GEOLOC | Veery.COLLECT | Veery.ROUTE_MATCH | Veery.POINT_OF_INTEREST | Veery.PREDICTION ); } }
This call can be made when the application starts (just after veery.serviceConnect()) but also after you have explained to the user why you require the Background Location right.
BACKEND and GEOPROFILE implies backend charges for every mobile where it is executed. Contact us for details.
onResume-onPause-onDestroy
Veery should know what is the status of your application (foreground, background, leaving).
In your MainActivity.java, add the following
public class MapsActivity extends AppCompatActivity { private final Veery veery = new Veery(this); @Override protected void onResume() { super.onResume(); // TODO : Let Veery know the ap has resumed veery.serviceResume(); } @Override protected void onPause() { super.onPause(); // TODO : Let veery know the app has paused veery.servicePause(); } @Override protected void onDestroy() { super.onDestroy(); try { // TODO : Let veery know the app is closing veery.serviceDisconnect(); } catch (Throwable t) { // Nothing to do } } }
AnyOtherActivity.java (Optional)
You can declare and use a Veery object in any Activity where you require geolocation or geoprofiling.
On all those classes you should respect the following template in order to let Veery know:
- When the activity is showed and disapear
- From when it should triggers the events your activity requires
TemplateActivity :
import android.location.Location; // add this import com.roofstreet.android.veery.*; // add this public class AnyOtherActivity extends Activity { private final Veery veery = new Veery(this); // add this protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); veery.serviceConnect(); // add this // Required only on Main Activity // veery.setApiKeySecret("SuPeRScrET12345789GhJ"); // FirebaseApp.initializeApp(this); // veery.setFirebaseToken(FirebaseInstanceId.getInstance().getToken()); // //veery.activate(Veery.GEOPROFILE); // Requires Android Veery 1.3.2 //veery.activate(Veery.BACKGROUND_GEOLOC | Veery.COLLECT | Veery.ROUTE_MATCH | Veery.POINT_OF_INTEREST | Veery.PREDICTION ); } @Override protected void onResume() { super.onResume(); veery.serviceResume(); // add this } @Override protected void onPause() { super.onPause(); veery.servicePause(); // add this } @Override protected void onDestroy() { super.onDestroy(); try { veery.serviceDisconnect(); // add this } catch (Throwable t) { } } }
Next Steps
Once this compile and runs, you are ready to ask to Veery about the geoprofile and predictions of trips of your users